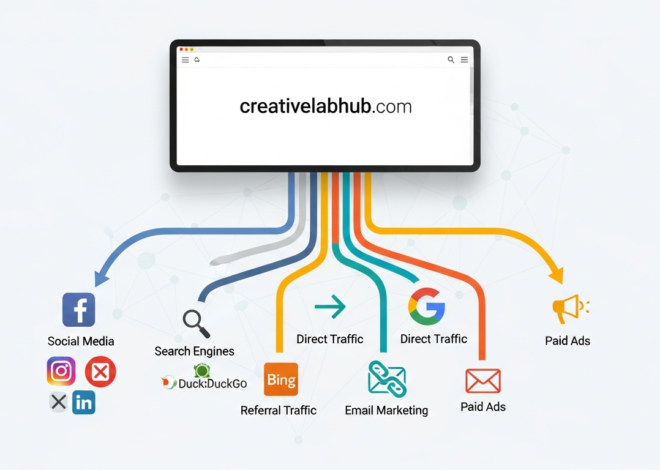
Retrieving Data: Ultimate Guide to Recovery (Stop Losing Files!) 2026
Introduction
You just clicked “save,” closed your document, and now it’s gone. Vanished. Your heart drops as you frantically search through folders, trying to find that critical file you spent hours working on. Sound familiar?
Retrieving data doesn’t have to be a nightmare. Whether you’ve accidentally deleted a file, experienced a system crash, or simply can’t remember where you saved something, there are practical solutions that actually work. In this guide, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about retrieving data from computers, smartphones, cloud services, and even damaged devices. You’ll discover simple methods that work right now, professional tools for serious recovery needs, and preventive strategies to protect your files in the future.
Let’s dive into the world of data retrieval and make sure you never lose another important file.
Understanding Data Retrieval: What You Need to Know
Before we jump into solutions, let’s clarify what retrieving data actually means. Data retrieval is the process of accessing, recovering, or extracting information that’s stored on a device or system. This could mean finding a file you misplaced, recovering deleted documents, or pulling data from a damaged hard drive.
Why Files Disappear
Files don’t just vanish into thin air. There’s always a reason. Understanding why helps you retrieve them faster.
Accidental deletion is the most common culprit. You hit delete without thinking, empty the recycle bin, and panic sets in. Software glitches can also hide or corrupt files. Sometimes your operating system fails to index new files properly. Hardware failures like damaged hard drives or corrupted storage devices can make data seem inaccessible.
Human error plays a huge role too. We save files to random locations, forget folder names, or accidentally overwrite important documents. The good news? Most of these situations are fixable.
How Data Storage Actually Works
When you delete a file, it doesn’t immediately disappear from your hard drive. Your computer simply marks that space as “available” for new data. The original file stays there until something overwrites it. This is why quick action matters when retrieving data.
Understanding this gives you hope. Even when files seem gone forever, they often still exist on your device. You just need the right approach to find them.
Basic Methods for Retrieving Data

Let’s start with the simplest solutions. These work for most everyday data retrieval situations.
Check Your Recycle Bin or Trash
This sounds obvious, but you’d be surprised how often it works. When you delete files on Windows, they go to the Recycle Bin first. Mac users have the Trash folder. These act as safety nets for accidental deletions.
Open your Recycle Bin or Trash. Sort by date deleted to find recent files quickly. Right-click the file you need and select “Restore” or “Put Back.” The file returns to its original location. Simple as that.
Empty your Recycle Bin regularly to free up space, but always double-check before you do. Once you empty it, retrieving data becomes more complicated.
Use Built-In Search Functions
Your computer has powerful search tools built in. Windows has File Explorer search. Mac has Spotlight. These can find files even when you’ve forgotten where they are.
On Windows, press Windows key + S and type your filename or keywords. Use file type filters like “kind:document” or “kind:picture” to narrow results. Search by date modified if you remember when you worked on the file.
Mac users should press Command + Space to open Spotlight. Type any detail you remember about the file. Spotlight searches content inside files too, not just filenames.
Check Cloud Sync Folders
If you use cloud storage services, check there immediately. Dropbox, Google Drive, OneDrive, and iCloud often sync files automatically. You might have a copy waiting in the cloud without even realizing it.
Log into your cloud service through a web browser. Check the main folder and the trash or deleted items section. Cloud services usually keep deleted files for 30 days before permanent deletion. This gives you a generous window for retrieving data.
Many cloud services also offer version history. If you accidentally saved over a file with the wrong version, you can restore earlier versions. This feature has saved me countless times.
Restore Previous Versions (Windows)
Windows includes a feature called “Previous Versions” that creates restore points automatically. If you’ve enabled this feature, you can recover earlier versions of files or folders.
Right-click the folder where your file was located. Select “Restore previous versions” from the menu. You’ll see a list of available restore points with dates and times. Choose the version from before your file disappeared. Click “Restore” to bring back the entire folder state from that point in time.
This method works best when System Protection is enabled on your drive. Check this setting regularly to ensure you have this safety net.
Use Time Machine (Mac)
Mac’s Time Machine is incredibly powerful for retrieving data. If you’ve set it up with an external drive, you have automatic backups of your entire system.
Connect your Time Machine drive. Click the Time Machine icon in your menu bar and select “Enter Time Machine.” A timeline appears on the right side of your screen. Navigate through dates to find when your file existed. Select the file and click “Restore.”
Time Machine backs up hourly for the past 24 hours, daily for the past month, and weekly for older months. This comprehensive coverage makes data retrieval straightforward for Mac users.
Advanced Techniques for Retrieving Data

When basic methods don’t work, it’s time for more advanced approaches. These require a bit more technical knowledge but offer powerful results.
Data Recovery Software
Professional data recovery software can retrieve data that seems permanently deleted. These programs scan your storage device at a deep level, finding files your operating system can’t see.
Popular options include Recuva (free for Windows), EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Disk Drill, and PhotoRec. Each has strengths depending on your situation.
Here’s how to use recovery software effectively. First, stop using the affected drive immediately. Every file you save might overwrite your deleted data. Download and install the recovery software on a different drive if possible. Run a quick scan first to see if your file appears. If not, perform a deep scan. This takes longer but finds more files.
Preview recoverable files before restoration. Save recovered files to a different drive than where they were lost. Never save them back to the same location during recovery.
Command Line Recovery
Technical users can leverage command-line tools for retrieving data. These built-in utilities sometimes work when graphical programs fail.
Windows users can try the “attrib” command to reveal hidden files. Open Command Prompt as administrator. Navigate to the folder where your file was located. Type “attrib -h -r -s /s /d .” and press Enter. This removes hidden, read-only, and system attributes from files, potentially making them visible again.
Linux users have powerful tools like “grep” and “dd” for searching and copying data from damaged filesystems. These require knowledge of Linux commands but offer incredible control.
Recovering from Damaged Drives
Physical drive damage presents unique challenges for retrieving data. If your hard drive makes clicking sounds, stops spinning, or isn’t recognized by your computer, the situation is serious.
Stop using the drive immediately. Continued use can cause more damage. For valuable data, consider professional recovery services. They have cleanroom environments and specialized equipment to extract data from severely damaged drives.
For less critical data or budget recovery, try these approaches. Connect the drive as an external device to another computer. Sometimes a different system can read drives the original computer couldn’t. Use recovery software designed for damaged drives. Programs like DMDE or R-Studio specialize in complex recovery scenarios.
If the drive isn’t recognized at all, freezing methods (putting the drive in a sealed bag in the freezer for a few hours) might work for mechanical failures. This is a last resort and doesn’t work for solid-state drives. The cold can temporarily allow a failing drive to spin long enough to copy critical files.
Database Recovery Techniques
Retrieving data from databases requires specialized knowledge. SQL databases, MongoDB, and other systems have specific recovery procedures.
Most database systems include transaction logs that record all changes. These logs can restore databases to specific points in time. Check your database documentation for backup and recovery procedures specific to your system.
For SQL Server, use the “RESTORE DATABASE” command with transaction logs. MySQL users can leverage binary logs for point-in-time recovery. Always maintain regular database backups with automated systems. Manual recovery is much harder than restoring from a good backup.
Retrieving Data from Mobile Devices
Smartphones and tablets present unique challenges for data retrieval. Their closed ecosystems make recovery different from traditional computers.
iPhone Data Recovery
iPhones sync with iCloud and iTunes/Finder automatically. Check your iCloud backup first. Go to Settings > [Your Name] > iCloud > Manage Storage > Backups. See if a recent backup exists that contains your data.
To restore from iCloud, you’ll need to reset your device and set it up again. This seems drastic, but it’s often the only way to retrieve data from iPhone backups. Alternatively, use third-party tools like Dr.Fone or iMobie PhoneRescue. These can extract specific files from iTunes backups without resetting your phone.
Photos and videos are usually safe if you’ve enabled iCloud Photos. They sync automatically and persist even after deletion for 30 days in the “Recently Deleted” album.
Android Data Recovery
Android offers more flexibility for retrieving data. Connect your phone to a computer via USB. Enable file transfer mode. You can browse the file system directly and search for your files.
Use Android’s Google Drive integration. Many apps backup data to Google Drive automatically. Check the Drive app for folders named after your apps. Google Photos backs up pictures automatically if you’ve enabled the feature.
For deleted files, try apps like DiskDigger or Dumpster. These work directly on your phone and can recover recently deleted photos and videos. Root access increases recovery chances but voids warranties and poses security risks.
Retrieving Data from Broken Phones
When screens break or phones won’t turn on, retrieving data becomes challenging. If the phone still functions but the screen is broken, connect it to a TV or monitor using an adapter. Many phones support video output through USB-C or HDMI.
Use a USB mouse with an adapter to navigate your phone and transfer files. For completely dead phones, professional recovery services can remove storage chips and extract data directly. This is expensive but works for irreplaceable data like family photos.
Cloud-Based Data Retrieval Strategies
Cloud storage has revolutionized how we protect and retrieve data. Understanding cloud platforms helps you maximize their recovery potential.
Google Drive Recovery
Google Drive keeps deleted files for 30 days in the Trash. Click the trash icon on the left sidebar. Find your file and right-click to restore it. After 30 days, files are permanently deleted.
Google Drive’s version history is powerful. Right-click any file and select “Version history.” You’ll see every saved version with timestamps. Restore any previous version with one click. This works for Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides, plus uploaded files that have been edited.
Google Drive also offers “Activity” tracking. This shows who accessed, edited, or deleted files. Use this to track down when and how data disappeared.
Dropbox Recovery Options
Dropbox keeps deleted files for 30 days (or 180 days with Dropbox Professional). Click “Deleted files” on the left sidebar to view them. Select files and click “Restore” to bring them back.
Dropbox’s rewind feature is incredible for retrieving data after major mistakes. It lets you roll back your entire Dropbox to a previous state within the past 30 days. This helps recover from ransomware, accidental mass deletions, or file corruption.
Access Dropbox rewind from the web interface. Click your profile picture, select “Settings,” then “Security.” Find “Rewind your Dropbox” and choose how far back to restore.
OneDrive and Microsoft 365 Recovery
OneDrive integrates tightly with Windows. Deleted files go to the OneDrive Recycle Bin for 30 days. Access it through the OneDrive website or the Windows File Explorer OneDrive section.
OneDrive for Business offers even longer retention and advanced recovery features. Administrators can restore deleted user accounts and all their data for up to 30 days after deletion.
Microsoft 365 apps like Word and Excel save versions automatically when files are stored in OneDrive. Click “File” > “Info” > “Version History” to see and restore previous versions.
Preventing Data Loss: Proactive Strategies
The best data retrieval strategy is never losing data in the first place. Implement these practices to protect your files.
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
Keep three copies of important data. Store them on two different types of media. Keep one copy offsite or in the cloud. This redundancy ensures you can always retrieve data no matter what happens.
Your working copy is the first version. An external hard drive backup is the second. Cloud storage is the third. If your computer crashes, you have the external drive. If your house burns down, you have the cloud copy.
Automate your backups. Manual backups fail because we forget to do them. Use built-in tools like Windows Backup, Time Machine, or third-party solutions like Acronis or Backblaze.
Regular Sync and Version Control
Enable automatic syncing for important folders. Cloud services can monitor specific folders and upload changes immediately. This creates real-time backups without any effort from you.
For creative work and projects, use version control systems. Git tracks every change to your files. GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket host your repositories online. If you make a mistake, you can roll back to any previous version.
This approach works beyond just code. Writers, designers, and researchers benefit from version history. Never worry about losing that paragraph you deleted three days ago.
Organized File Management
Create a logical folder structure. Know where files belong before you save them. Consistent organization makes files easier to find and reduces the need for data retrieval.
Use descriptive filenames with dates. “Project Report 2026-01-09.docx” is much better than “report.docx.” Add keywords that you’ll remember when searching later.
Implement a consistent naming convention across your work. This might seem tedious, but it saves hours when retrieving data months or years later.
Test Your Backups Regularly
Backups are worthless if they don’t work when you need them. Test your backup systems quarterly. Try restoring random files. Verify that backups are actually running on schedule.
I learned this lesson the hard way. I thought my backups were running for months. When my drive failed, I discovered the backup software had stopped working after an update. The last good backup was five months old. Don’t let this happen to you.
Check backup logs. Ensure all important files are included. Update backup settings when you add new critical folders or files.
When to Call a Professional
Some data retrieval situations require professional help. Knowing when to stop DIY efforts prevents making things worse.
Signs You Need Expert Help
Physical drive damage with clicking sounds means mechanical failure. Professionals have cleanroom facilities to open drives safely. Attempting this yourself will destroy your data permanently.
If recovery software finds nothing after deep scans, the data might be overwritten or the drive might have complex damage. Professionals use advanced tools not available to consumers.
For business-critical data, legal evidence, or irreplaceable personal files like wedding videos, don’t take chances. Professional recovery services offer the best chance of success.
What Professional Recovery Involves
Professional services evaluate your drive first. They provide a cost estimate based on the damage severity and recovery chances. Prices range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars depending on the situation.
The process happens in cleanroom environments for physically damaged drives. Technicians might replace failed components, image the drive bit-by-bit, or use specialized hardware to read damaged platters.
Success rates vary. Logical damage (accidental deletion, corruption) has high recovery rates. Physical damage outcomes depend on the extent of damage. No reputable company guarantees 100% recovery, but they’ll tell you realistic expectations upfront.
Choosing a Recovery Service
Research companies thoroughly. Read reviews and check Better Business Bureau ratings. Avoid services that guarantee 100% recovery or have no physical location.
Ask about their “no data, no charge” policy. Reputable companies don’t charge if they can’t recover your data. Get everything in writing before authorizing work.
Understand turnaround times. Standard service takes days to weeks. Expedited emergency service costs significantly more but delivers results in 24-48 hours.
Common Data Retrieval Mistakes to Avoid
Knowing what not to do is just as important as knowing correct procedures. These mistakes make retrieving data harder or impossible.
Don’t Keep Using the Device
The biggest mistake people make is continuing to use a device after data loss. Every file you save might overwrite your deleted data. Stop immediately when you realize data is missing.
This applies to all devices. Don’t browse the internet, don’t save new files, don’t install recovery software on the same drive. Use a different computer or device for your recovery efforts.
I’ve seen people lose data permanently because they “just needed to finish this one thing” before starting recovery. That one thing erased their precious files forever.
Don’t Skip the Easy Solutions First
People often jump straight to expensive software or professional services without checking simple solutions. Always start with the Recycle Bin, cloud backups, and built-in search functions.
I once spent an hour helping a friend find an “important lost document.” It was sitting in their Downloads folder with a different filename than they remembered. Two minutes of searching would have found it.
Work through solutions systematically from simplest to most complex. You’ll save time and money.
Don’t Ignore Warning Signs
Drives don’t fail suddenly without warning. Clicking sounds, slow performance, frequent crashes, and file corruption are all red flags. When you notice these signs, backup immediately and plan for replacement.
Retrieving data is much easier when you act on warnings rather than waiting for complete failure. Back up your files the moment you suspect problems.
Denial is expensive. That weird noise won’t fix itself. Address it before it becomes a crisis.
Conclusion
Retrieving data doesn’t have to be mysterious or overwhelming. Start with simple solutions like checking your Recycle Bin, searching thoroughly, and exploring cloud backups. Most data recovery situations resolve with basic methods.
For more serious cases, recovery software and professional services can retrieve data from damaged drives and complex scenarios. The key is acting quickly and avoiding actions that might overwrite your lost files.
Remember, the best approach is preventing data loss entirely. Implement the 3-2-1 backup rule, enable automatic syncing, and test your backups regularly. These habits ensure you’ll never face a true data disaster.
What data recovery story do you have? Have you successfully retrieved data from a disaster, or learned a hard lesson about backups? Share your experience in the comments – your story might help someone else avoid data loss.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does data retrieval typically take?
Simple recovery from Recycle Bin or cloud trash takes seconds. Recovery software scans need 30 minutes to several hours depending on drive size. Professional services range from 24 hours for expedited service to 2-3 weeks for standard cases. Complex physical damage recovery can take a month or more.
Can I retrieve data after formatting a drive?
Yes, often you can. Formatting marks all space as available but doesn’t erase data immediately. Quick formats are easiest to recover from. Full formats are harder but still possible until data gets overwritten. Stop using the drive immediately and use professional recovery software.
Is it possible to retrieve data from a dead SSD?
SSDs are more challenging than traditional hard drives. If the controller chip fails, professional recovery is your only option. Some SSDs have built-in encryption that makes recovery impossible if the controller dies. This is why backups are critical for SSD users.
How much does professional data recovery cost?
Prices vary widely based on damage severity. Simple logical recovery starts around $300-500. Physical damage recovery ranges from $500-2,500. Complex cases requiring cleanroom work can cost $3,000-5,000 or more. Always get a free evaluation and quote before authorizing work.
What’s the success rate for retrieving deleted files?
Recently deleted files have high recovery rates (80-90%) if you act quickly. Files deleted months ago have lower rates depending on how much new data was written. Overwritten data cannot be recovered. Physical damage reduces success rates unpredictably.
Can I retrieve data from a water-damaged device?
Sometimes, but timing matters. For phones or laptops exposed to water, turn them off immediately. Don’t try to power them on. Remove the battery if possible. Dry the device with professional help. Water damage often affects circuits rather than storage, so professional recovery services can sometimes extract data from the storage chip directly.
Do recovery software programs actually work?
Legitimate recovery programs work well for their intended purposes. Recuva, EaseUS, and Disk Drill have proven track records. They work best for recently deleted files on functioning drives. Be cautious of scam software that claims miraculous recovery rates. Stick with established brands with good reviews.
How can I tell if my backup is working correctly?
Regularly test your backup by restoring a random file. Check backup logs for errors or warnings. Verify that all critical folders are included in your backup plan. Set calendar reminders to review your backup system quarterly. A backup you haven’t tested is just wishful thinking.
What’s the difference between backup and sync?
Backup creates separate copies of your files that exist independently. If you delete a file on your computer, the backup copy remains. Sync mirrors changes across all connected devices. Deleting a synced file removes it everywhere. Use both: sync for convenience, backup for protection.
Is cloud storage safe for important data?
Cloud storage is generally very safe with encryption and redundant storage. Major providers like Google, Dropbox, and Microsoft invest heavily in security. However, use two-factor authentication and strong passwords. Don’t rely solely on cloud storage – follow the 3-2-1 rule with local backups too.
Also Read : Marvel Rivals Rank Distribution